In the United States, the number of single mothers has been steadily increasing over the years. Single motherhood is now a common aspect of American family life, representing a significant portion of all family structures. But have you ever wondered which state has the most single mothers? Understanding the geographic distribution of single mothers across the U.S. can shed light on broader socioeconomic trends and help us identify the states where single mothers face the most significant challenges.
What State Has the Most Single Mothers?
Top 5 States with the Highest Number of Single Mothers
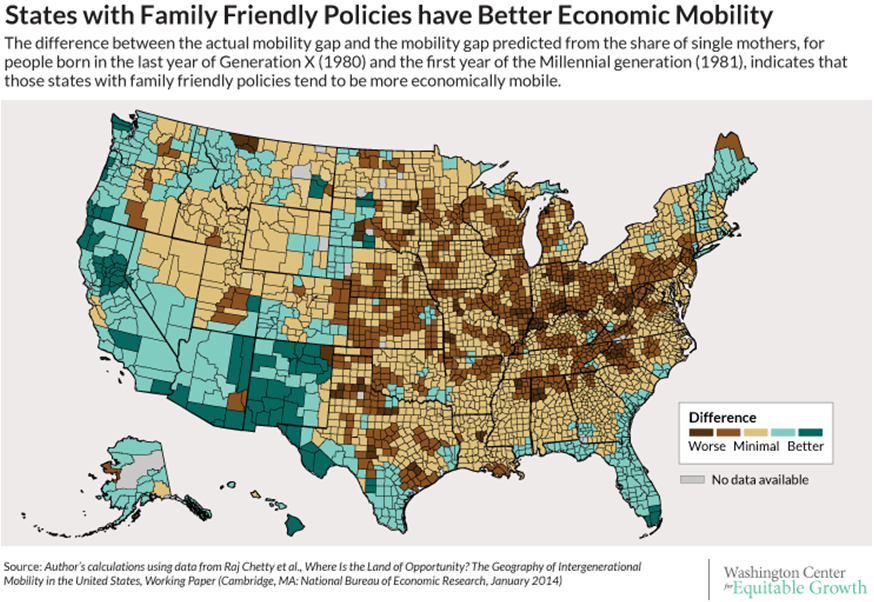
When looking at the U.S. states with the highest percentage of single mothers, a clear pattern emerges. Southern states tend to have higher rates of single motherhood compared to other regions. According to the latest data from the U.S. Census Bureau, these are the top five states with the most single mothers:
| State | Percentage of Single-Parent Households | Rank |
|---|---|---|
| Mississippi | 45% | 1 |
| Louisiana | 42% | 2 |
| New Mexico | 41% | 3 |
| Arkansas | 40% | 4 |
| Alabama | 39% | 5 |
Mississippi consistently ranks at the top, with nearly half of all households headed by a single mother. This trend is mirrored by other Southern states like Louisiana and Arkansas, which also have high percentages of single-parent families. These states not only have high rates of single motherhood but also share similar economic challenges, such as higher poverty rates and limited access to social services.
Why Do These States Have Higher Numbers of Single Mothers?
There are several contributing factors that explain why states like Mississippi, Louisiana, and Arkansas have such high percentages of single mothers. Let’s break down some of the key reasons:
- Economic Factors:
- Poverty Rates: Mississippi and Louisiana have some of the highest poverty rates in the country, which correlates with a higher likelihood of single motherhood. Economic instability can discourage marriage and make it more difficult for single mothers to escape poverty.
- Job Availability: These states often have limited job opportunities, particularly for women without higher education. As a result, many single mothers struggle to find stable employment, which exacerbates their financial difficulties.
- Cultural Factors:
- Family Structure Norms: In some regions, traditional family structures are more common, and yet paradoxically, they also experience higher rates of single motherhood. Factors like early marriage and early childbearing, followed by higher divorce rates, contribute to these numbers.
- Marriage Rates: Lower marriage rates, especially among younger women, have contributed to higher single motherhood rates. In some states, marriage is no longer seen as a prerequisite for starting a family.
- Social Safety Nets:
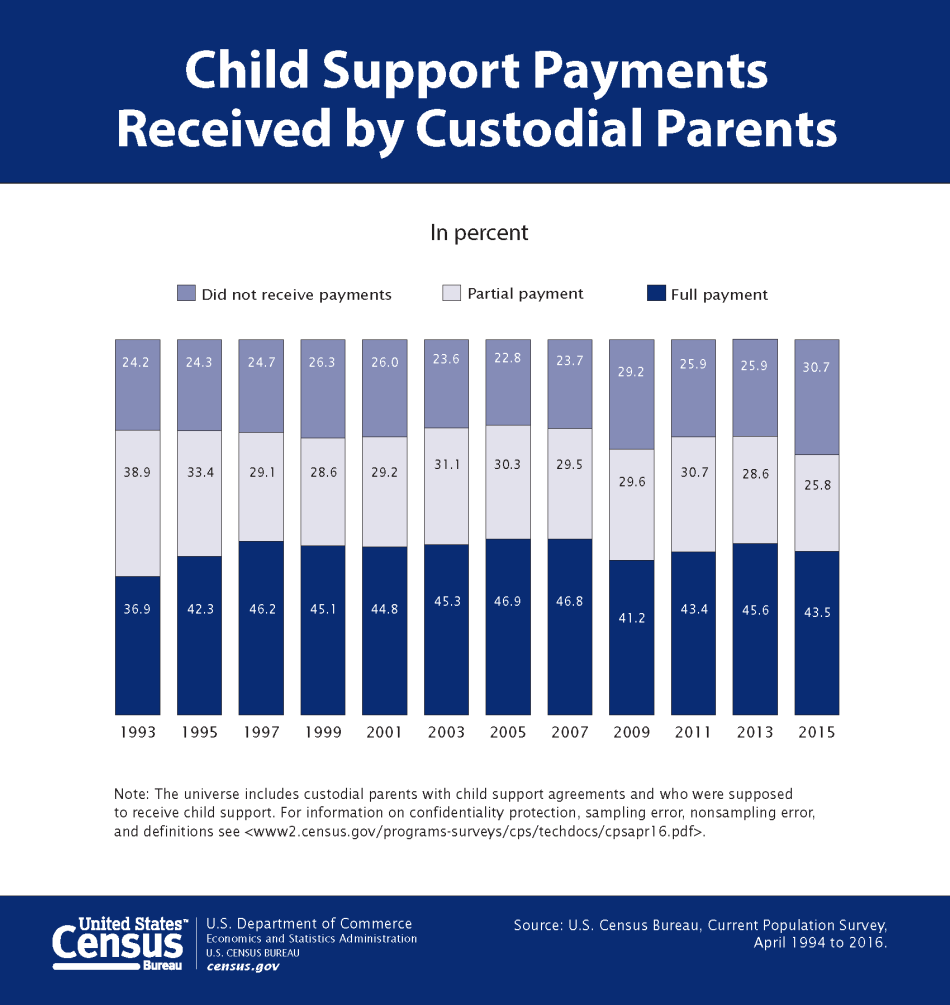
- Welfare and Assistance Programs: States with fewer social safety nets, such as affordable child care, health care, and housing assistance, tend to have higher rates of single motherhood. In states like Mississippi and Louisiana, the support systems for single mothers are often limited, making it harder for women to provide for their children without a partner’s support.
- Healthcare Access: Access to affordable healthcare, including reproductive health services, is often lacking in these states. Limited access to contraception and family planning services can lead to higher unplanned pregnancy rates, which contributes to single motherhood.
Urban vs. Rural Areas: Where Are Single Mothers Concentrated?
Another important factor when analyzing the geography of single motherhood is the distinction between urban and rural areas. Single mothers are more concentrated in urban areas due to better access to job opportunities and services, such as schools and healthcare. However, rural areas also face their own unique challenges:
- Urban Areas: Cities often have higher concentrations of single mothers, as they provide better access to jobs, public transportation, and child care services. Urban centers in states like New York and California have large populations of single mothers, even though these states don’t rank highest overall.
- Rural Areas: In states like Mississippi and Arkansas, single mothers in rural areas may struggle more due to fewer job opportunities, lack of reliable public transportation, and less access to health care and educational resources. This isolation can make it even harder for rural single mothers to achieve economic stability.
While single motherhood is more prevalent in urban areas, rural single mothers face unique challenges that contribute to their economic vulnerability. The lack of infrastructure in these regions can make it more difficult for them to raise their children without the financial support of a partner.